Water is essential to life, and its quality can significantly impact health and well-being. With increasing concerns about contaminants in drinking water, reverse osmosis has emerged as a popular solution. This advanced filtration technology offers crystal-clear hydration by removing impurities at a molecular level. Whether you’re considering an RO system for your home or exploring options for commercial or industrial use, understanding how reverse osmosis works will empower you to make informed choices.
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a powerful water purification process that uses a semipermeable membrane to filter out contaminants. This technology works by applying pressure to push water through the membrane, which traps impurities while allowing clean water to pass through.
The effectiveness of RO systems lies in their ability to remove various substances, including salts, bacteria, and heavy metals. This makes them ideal for producing high-quality drinking water free from harmful elements.
Unlike traditional filtration methods, reverse osmosis targets microscopic particles. The result is pure, great-tasting water that you can trust.
Many homeowners are opting for RO systems not only for better taste but also for peace of mind regarding health concerns. As awareness of tap water quality grows, more people are investing in this advanced solution to ensure safe hydration every day.
Industrial RO
(RO) Systems are essential for large-scale water purification. These systems effectively remove impurities, contaminants, and dissolved solids from water sources.
Industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and manufacturing rely on high-quality water for their operations. With increasingly stringent water quality regulations, industrial RO has become a crucial investment.
The technology operates by forcing water through semipermeable membranes under pressure. This process ensures that only clean water passes through while blocking harmful substances.
Durability is key in industrial settings. Many of these systems are designed to handle heavy workloads and continuous operation. They can also be customized to meet specific industry needs.
Maintenance is vital for optimal performance; regular monitoring ensures longevity and efficiency. As industries continue to grow, demand for effective solutions such as industrial RO is likely to increase significantly.
Commercial Reverse Osmosis
Commercial reverse osmosis systems are game-changers for businesses seeking high-quality water. These systems are specifically designed for restaurants, hotels, and factories.
As concerns about water quality grow, commercial RO units offer a reliable solution. They effectively remove impurities like chlorine, heavy metals, and other contaminants that can affect taste and safety.
Installing a commercial RO system improves beverage quality in cafes and enhances food prep standards in kitchens. It also helps industries reduce operational costs by minimizing equipment maintenance costs associated with poor water quality.
Moreover, these systems offer scalability. As a business grows or changes its operations, so too can the RO system adapt to meet new demands without compromising performance.
Choosing the right setup ensures efficiency while delivering pure water, consistently critical for any commercial operation aiming for excellence.
In commercial applications, reverse osmosis systems are essential for ensuring water quality. Businesses that rely on high-purity water, such as restaurants, hotels, and laboratories, often turn to RO systems for their efficiency and effectiveness. These systems offer a reliable solution for maintaining the integrity of food preparation processes or scientific experiments.
Using commercial reverse osmosis
units allows businesses to meet health standards while reducing waste from bottled water. Additionally, with customizable filtration options, companies can tailor their RO setups to address specific contaminants found in local water supplies.
The investment in a commercial RO system pays off through improved product quality and customer satisfaction. Whether it’s providing crystal-clear ice cubes for drinks or ensuring clean equipment-washing procedures, the advantages are clear.
For those considering installing such systems, it’s vital to consider factors such as capacity needs and maintenance requirements. With proper care and regular monitoring of your reverse osmosis unit, you can enjoy consistent performance that meets your business demands without compromise.
Choosing the right setup not only enhances operational efficiency but also promotes sustainability by minimizing plastic usa, a crucial factor in today’s eco-conscious market landscape. Adopting a robust commercial RO system signifies a commitment to both quality service and environmental responsibility.
Clean, safe, and great-tasting water is essential whether you’re a homeowner, a business owner, or an industrial operator. Today’s water sources contain more contaminants than ever before: chemicals, heavy metals, microplastics, TDS (total dissolved solids), pesticides, and even harmful microbes. These contaminants affect health, food quality, appliances, and industrial processes.
This is why more people worldwide are relying on a reverse osmosis water filter. It is the gold-standard water purification technology for home use, commercial applications, and large-scale industrial operations. When combined with modern filtration components like an RO membrane, UV, carbon filtration, and remineralization stages, reverse osmosis delivers unmatched purity and long-term value.
In this complete guide, we break down:
- What is RO?
- Reverse osmosis meaning (simple explanation)
- Why RO systems outperform traditional filters
- Reverse osmosis for home use
- Commercial RO systems
- Industrial RO systems
- Key benefits: TDS removal, chemical removal, desalination, and more
- RO maintenance and installation cost
- RO vs UV vs UF
- How to choose the right reverse osmosis filter system (under-sink RO, tankless RO system, alkaline RO water system, etc.)
This article is written in a marketing + conversion tone, optimized for all audiences — homeowners, businesses, and industries — and includes all primary, secondary, and LSI keywords.
1. What Is Reverse Osmosis? (RO Meaning)
Reverse Osmosis Meaning
Reverse osmosis is a water treatment technology that pushes water through a semipermeable RO membrane. The membrane removes impurities at the molecular level, leaving only pure water molecules behind.
Reverse osmosis eliminates a wide range of contaminants, including:
- TDS (Total Dissolved Solids)
- Arsenic, fluoride, chromium, lead, mercury
- Bacteria and viruses (with UV)
- Chemicals, pesticides, and VOCs
- Chlorine and chloramine
- Microplastics
- Hardness-causing minerals
- Odor and taste issues
An RO membrane filters particles up to 0.0001 microns, which is significantly more effective than standard water purifier technologies.
Why Reverse Osmosis Is Superior
Many consumers compare RO vs UV vs UF:
Technology Removes Chemicals, Removes TDS, and Removes Microbes For
RO System Yes Yes Yes (with UV) Home, commercial, industrial
UV Purifier No No Yes Homes with microbiological contamination
UF Filter Limited No Some bacteria Low TDS water
Reverse osmosis is the only water purification method that removes both TDS and chemical contaminants, providing safe, fresh water for drinking, cooking, commercial use, and industrial processes.

2. Why Reverse Osmosis Water Filters Are in High Demand
Water contamination is at an all-time high. Aging pipelines, chemical runoff, industrial waste, and increasing microplastic pollution have made reverse osmosis a necessity — not a luxury.
Benefits of a Reverse Osmosis System
- Eliminates 95–99% of impurities
- Provides consistently clean water
- Improves taste and odor
- Offers complete TDS removal
- Supports healthy cooking and drinking
- Protects appliances from scaling
- Reduces reliance on bottled water
- Cost-effective long-term
- Works for home, commercial, and industrial needs
Reverse osmosis is simply the most complete water purification technology in the world.
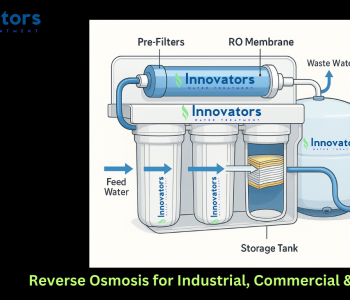
3. How a Reverse Osmosis Filter System Works
A typical reverse osmosis filter system includes multiple stages:
1. Sediment Filter
Removes dirt, sand, and rust.
2. Activated Carbon Filter
Removes chlorine, chemicals, pesticides, and organic compounds.
3. RO Membrane
The core of the RO system removes TDS, heavy metals, salts, nitrates, fluoride, and microplastics.
4. Storage Tank (for under-sink RO)
Stores purified water.
5. Post Carbon Filter
Polishes water for better taste and aroma.
Optional Advanced Stages
- UV filtration for bacteria and viruses
- Alkaline RO water filters for pH balancing and remineralization
- TDS controller
- Sediment pre-treatment for industrial RO systems
This is why RO delivers premium water quality with consistent performance.
4. Reverse Osmosis for Home Use: The Best Water Purification Option
Homeowners increasingly choose RO systems because they provide:
- Safe drinking water
- Lower TDS
- Better taste
- Protection for children and elderly family members
- Fresh water for cooking and beverages
- No more bottled water costs
Popular Home RO System Options
- Under Sink RO
- Most common. Discreet, compact, and effective.
- Tankless RO System
- Modern, fast, efficient. Saves space and reduces water waste.
- Alkaline RO Water System
- Adds healthy minerals, such as calcium and magnesium.
- RO + UV + UF Combination
- Best for well water.
- Countertop RO Purifier
- Portable. No installation needed.
Home Applications
- Drinking
- Cooking
- Coffee, tea, and beverages
- Baby formula
- Aquariums
- Appliances like kettles and humidifiers
Reverse osmosis for home use ensures the highest water purity at every sip.
5. Commercial RO System: Designed for Businesses
A commercial RO system is essential for:
- Restaurants
- Cafes
- Hotels
- Coffee shops
- Offices
- Gyms
- Schools
- Clinics and dental practices
- Salons
- Bakeries
Why Businesses Need Commercial Water Filtration
- Consistent water quality improves food & beverages
- Equipment lasts longer (coffee machines, boilers, dishwashers)
- Customers trust clean drinking water
- Eliminates plastic bottles
- Meets health & safety regulations
- Cuts operational costs
- Supports branded water solutions (restaurants, offices)
Commercial RO System Features
- High flow rate (100–2,000 LPH)
- Multi-stage filtration
- Long-life RO membranes
- Robust construction
- Optional UV sterilization
- Smart TDS monitoring
A commercial RO system enhances a brand’s quality, customer experience, and operational reliability.
6. Industrial RO System: Heavy-Duty Water Treatment Solutions
Large-scale industrial applications require high-capacity, durable, and precise water treatment. An industrial RO system supports large operations with consistent purity.
Industries Using Industrial RO Systems
- Pharmaceuticals
- Chemical plants
- Food and beverage manufacturing
- Textile processing
- Power plants
- Boiler feed water
- Cooling towers
- Electroplating
- Microelectronics manufacturing
- Dairy & ice production
- Industrial desalination facilities
Capacity
5,000 – 100,000+ liters per hour.
Why Industries Choose RO
- Ensures consistent water parameters
- Reduces scaling in boilers and equipment
- Supports production quality
- Reduces downtime
- Meets ISO and regulatory water standards
- Enables desalination for coastal industries
- Long-term cost savings
Industrial RO systems use advanced components and automation, including:
- High-pressure multi-stage pumps
- FRP or SS skids
- Programmable logic controllers (PLC)
- Energy recovery units
- Large-diameter RO membranes
This ensures reliable 24/7 operation.

7. RO Plant Manufacturer Insights
If your business manufactures or distributes RO plants, the market is massive.
Buyers look for:
- Certification and quality
- Strong RO membrane performance
- Low RO installation cost
- Low RO maintenance requirements
- Spare parts availability
- Service support
- Customizable capacity
Offering home, commercial, and industrial water purifier solutions expands your market reach.
8. TDS Removal: Why RO Is the Only Reliable Solution
Reverse osmosis is the most powerful TDS removal technology available.
TDS includes:
- Mineral salts
- Metals
- Chemicals
- Industrial waste
- Organic contaminants
High-TDS water tastes salty, metallic, or chalky — and may cause health issues.
Only reverse osmosis can reliably bring TDS to an optimal level (50–150 ppm).
9. Reverse Osmosis vs UV vs UF
RO removes dissolved salts and chemicals
UV kills microbes
UF removes some particles but not TDS
RO remains the most complete purification method.
10. Reverse Osmosis Maintenance & Installation Cost
RO Installation Cost
- Home RO: $50–$150
- Commercial RO: $100–$300
- Industrial RO: Custom, based on size
RO Maintenance
- Sediment filter: every 6–12 months
- Carbon filter: every 6–12 months
- RO membrane: every 2–3 years
- UV lamp: yearly
- Industrial RO: scheduled maintenance routines
Proper maintenance ensures long membrane life and consistent purity.
11. How to Choose the Right Reverse Osmosis Water Filter
For Homeowners
- Under-sink RO
- Tankless RO system
- Alkaline RO water purifier
Businesses
- Commercial RO system
- Medium-to-high flow rate
- UV + carbon add-ons
For Industry
- Industrial RO system
- High-pressure pumps
- Multi-stage treatment
- Desalination capabilities
12. Final Verdict: Reverse Osmosis Is the Best Water Purification Technology for Every Sector
A reverse osmosis water filter is the most reliable, versatile, and future-ready technology for:
- Home drinking water
- Commercial water filtration
- Industrial desalination
- High-volume water treatment solutions
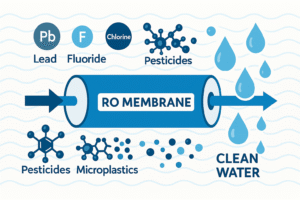
What specific contaminants can reverse osmosis systems effectively remove from water?
Contaminants Removed by Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems
Reverse osmosis systems are highly effective at removing a wide range of contaminants from water. Some of the key pollutants they can eliminate include:
- Dissolved Solids: Including salts, minerals, and heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and arsenic.
- Microorganisms: Bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, which can be harmful to health.
- Chlorine and Chloramine: Often used in municipal water systems for disinfection.
- Pesticides and Herbicides: These can be harmful if ingested over time.
- Fluoride: Some RO systems can remove fluoride, though this depends on the specific membrane.
- Nitrates and Nitrites: Common contaminants in agricultural areas.
- Sulfates: These can cause a bitter taste in water.
- Other Organic Compounds: Pesticides, industrial chemicals, and VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds).
RO systems work by pushing water through a semipermeable membrane that filters out particles, allowing only clean water molecules to pass through while trapping contaminants.
How does the maintenance process for an RO system typically work?
Maintenance Process for an RO System
Maintaining a reverse osmosis system is essential to ensuring its efficiency and longevity. The typical maintenance steps include:
- Replacing Filters: RO systems have pre-filters, post-filters, and the RO membrane. The pre-filters (usually sediment and carbon filters) should be replaced every 6 to 12 months, depending on water quality and usage. The RO membrane typically lasts 2 to 3 years before needing replacement.
- Cleaning the RO Membrane: The RO membrane can accumulate scale or biofouling over time. It needs to be cleaned periodically (every 1 to 2 years) to prevent clogging and to maintain efficiency.
- Checking Water Pressure: The water entering the RO system must be within a specified range for optimal operation.
- Sanitizing the System: An annual sanitization is recommended to ensure the system is free from bacteria or mold buildup, especially in humid environments.
- Monitoring System Performance: Keeping an eye on clean water output, checking for leaks, and ensuring the flow rate remains consistent helps identify issues early.
What are the long-term cost implications of installing a reverse osmosis system compared to traditional water filtration methods?
Long-term Cost Implications of RO Systems vs. Traditional Water Filtration
When comparing reverse osmosis systems to traditional filtration methods, there are several long-term cost implications to consider:
- Initial Installation Cost: RO systems tend to have higher upfront installation costs than traditional water filters. The cost of an RO system varies depending on complexity (e.g., under-sink vs. whole-house systems) and features.
- Replacement Filters and Membranes: The ongoing costs for RO systems can be higher than traditional filters because of the need to replace the pre-filters, post-filters, and the RO membrane. For example, membrane replacement is needed every 2-3 years, while filters might need replacement every 6-12 months.
- Water Waste: RO systems typically waste 3 to 4 gallons of water for every gallon of purified water produced. This can result in higher water utility bills over time, particularly in areas with high water costs.
- Energy Usage: Some advanced RO systems, especially those that include a pressurized tank or a booster pump, can also increase energy usage, adding to operational costs.
- Long-Term Savings: Despite higher maintenance and initial costs, RO systems can save money in the long term by replacing bottled water purchases, especially in areas with poor-quality tap water. Over time, the cost of bottled water can add up, and an RO system offers a more sustainable, cost-effective alternative.